- HOME
- News & Events
- Publications
- 【Publications】Extracellular Vesicles From Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Containing Annexin A6 Induce...
Publications
【Publications】Extracellular Vesicles From Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Containing Annexin A6 Induces FAK-YAP Activation by Stabilizing β1 Integrin, Enhancing Drug Resistance
July 15 2020
Takatsugu Ishimoto
Paper information
Uchihara T, Miyake K, Yonemura A, Komohara Y, Itoyama R, Koiwa M, Yasuda T, Arima K, Harada K, Eto K, Hayashi H, Iwatsuki M, Iwagami S, Baba Y, Yoshida N, Yashiro M, Masuda M, Ajani JA, Tan P, Baba H*, Ishimoto T.*
(*corresponding authors)
Extracellular Vesicles From Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Containing Annexin A6 Induces FAK-YAP Activation by Stabilizing β1 Integrin, Enhancing Drug Resistance
Cancer Res. 2020 Jun 30:canres.3803.2019. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-3803. Online ahead of print.
Highlights
-
CAF amount in GC tissues was significantly correlated with poor prognosis in a large cohort of 335 GC patients.
-
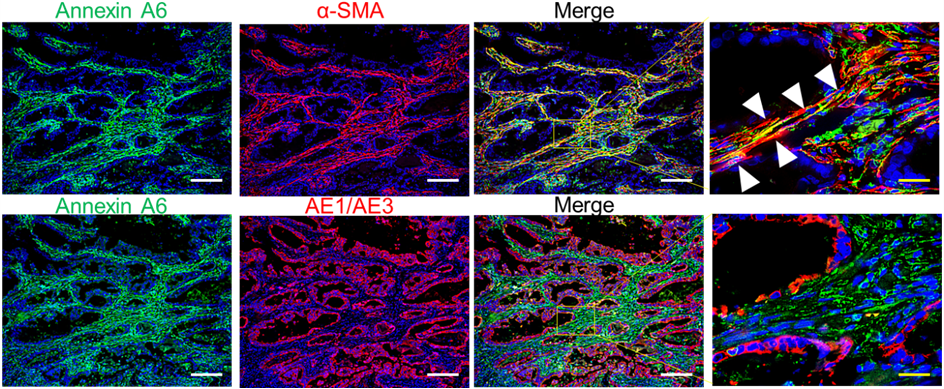
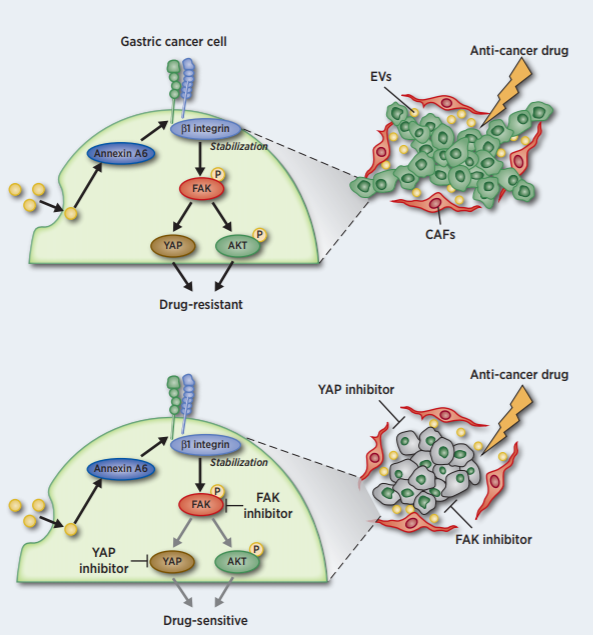
CAF-EVs induced the tubular network formation and drug resistance of GC cells in the extracellular matrix (ECM) through β1integrin -FAK-YAP activation.
-
Comprehensive proteomic analysis revealed that AnnexinA6 in CAF-EVs as a critical factor for the tubular network formation and drug resistance of GC cells in the ECM.
- Chemical inhibition by FAK or YAP inhibitors but not an AKT inhibitor efficiently attenuated CAF-EV-induced drug resistance of GC cells in vitro and in vivo.
Abstract
Extracellular vesicles (EV) from cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF) are composed of diverse payloads. Although CAF impact the aggressive characteristics of gastric cancer (GC) cells, the contribution of CAF-EV to GC progression has not been elucidated. Here we investigated the molecular mechanism of the changes in GC characteristics induced by CAF-EV. CAF abundance in GC tissues was associated with poor prognosis of GC patients receiving chemotherapy. Moreover, CAF-EV induced tubular network formation and drug resistance of GC cells in the extracellular matrix (ECM). Comprehensive proteomic analysis of CAF-EV identified annexin A6 plays a pivotal role in network formation and drug resistance of GC cells in the ECM via activation of β1 integrin-focal adhesion kinase (FAK)-YAP. A peritoneal metastasis mouse model revealed that CAF-EV induced drug resistance in peritoneal tumors, and inhibition of FAK or YAP efficiently attenuated GC drug resistance in vitro and in vivo. These findings demonstrate that drug resistance is conferred by annexin A6 in CAF-EV and provide a potential avenue for overcoming GC drug resistance through the inhibition of FAK-YAP signaling in combination with conventional chemotherapeutics.