- HOME
- News & Events
- Publications
- 【Publications】Chromatin modifier Hmga2 promotes adult hematopoietic stem cell function and blood reg...
Publications
【Publications】Chromatin modifier Hmga2 promotes adult hematopoietic stem cell function and blood regeneration in stress conditions
June 19 2024
Lab: Goro Sashida
Paper information
Tile:
Chromatin modifier Hmga2 promotes adult hematopoietic stem cell function and blood regeneration in stress conditions
Sho Kubota, Yuqi Sun, Mariko Morii, Jie Bai, Takako Ideue, Mayumi Hirayama, Supannika Sorin, Eerdunduleng, Takako Yokomizo-Nakano, Motomi Osato, Ai Hamashima, Mihoko Iimori, Kimi Araki, Terumasa Umemoto, Goro Sashida
The EMBO Journal May 29, 2024 DOI: 10.1038/s44318-024-00122-4.
Highlights
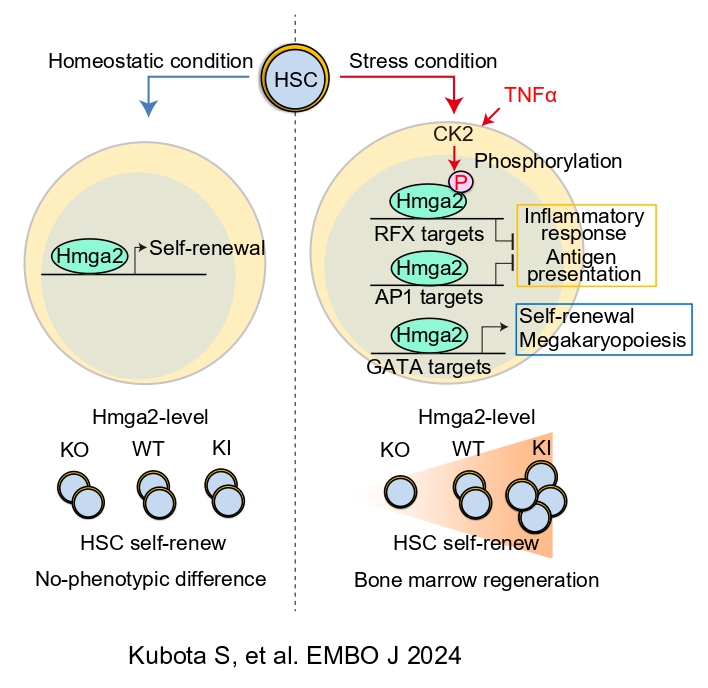
- Conditional depletion of Hmga2 does not affect steady-state hematopoiesis but impairs HSC response to 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) in adult mice.
- Under stress, CK2 kinase phosphorylates Hmga2 in TNF-α-dependent manner, promoting its chromatin binding and repression of inflammatory genes by transcription factor Rfx5.
-
The identified stress-induced Hmga2 gene signature is activated in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells of human myelodysplastic syndrome patients.
Abstract:
The molecular mechanisms governing the response of hematopoetic stem cells (HSCs) to stress insults remain poorly defined. Here, we investigated the effects of conditional knock-out or overexpression of Hmga2 (High mobility group AT-hook 2), a transcriptional activator of stem cell genes in fetal HSCs. While Hmga2 overexpression did not affect adult hematopoiesis under homeostasis, it accelerated HSC expansion in response to injection with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) or in vitro treatment with TNF-a. In contrast, HSC and megakaryocyte progenitor cell numbers were decreased in Hmga2 KO animals. Transcription of inflammatory genes was repressed in Hmga2-overexpressing mice injected with 5-FU, and Hmga2 bound to distinct regions and chromatin accessibility was decreased in HSCs upon stress. Mechanistically, we found that casein kinase 2 (CK2) phosphorylates the Hmga2 acidic domain, promoting its access and binding to chromatin, transcription of anti-inflammatory target genes, and the expansion of HSCs under stress conditions. Notably, the identified stress-regulated Hmga2 gene signature is activated in hematopoietic stem progenitor cells of human myelodysplastic syndrome patients. In sum, these results reveal a TNF-a/CK2/phospho-Hmga2 axis controlling adult stress hematopoiesis.
Graphical abstract