- HOME
- News & Events
- Publications
- 【Publications】Intracellular MUC20 variant 2 maintains mitochondrial calcium homeostasis and enhances...
Publications
【Publications】Intracellular MUC20 variant 2 maintains mitochondrial calcium homeostasis and enhances drug resistance in gastric cancer
July 15 2022
May;25 2022
Takatsugu Ishimoto
Paper information
Title:
Intracellular MUC20 variant 2 maintains mitochondrial calcium homeostasis and enhances drug resistance in gastric cancer
Lingfeng Fu, Atsuko Yonemura, Noriko Yasuda-Yoshihara, Terumasa Umemoto, Jun Zhang, Tadahito Yasuda, Tomoyuki Uchihara, Takahiko Akiyama, Fumimasa Kitamura, Kohei Yamashita, Yuya Okamoto, Luke Bu, Feng Wei, Xichen Hu, Yang Liu, Jaffer A. Ajani, Patrick Tan, Hideo Baba*, Takatsugu Ishimoto*
(*corresponding authors)
Gastric Cancer 2022 May;25(3):542-557.
doi: 10.1007/s10120-022-01283-z.
Highlights
- We analyzed a comprehensive GC cell line database and identified the specifically expressed mucin (MUC) in gastric SRCC.
- Specific transcript variant of MUC20 (MUC20v2) was dominantly expressed in the cytoplasm of gastric SRCC cells.
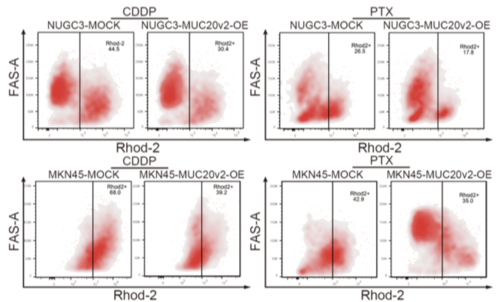
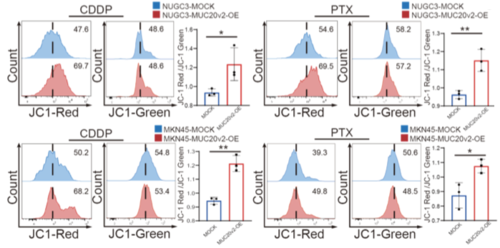
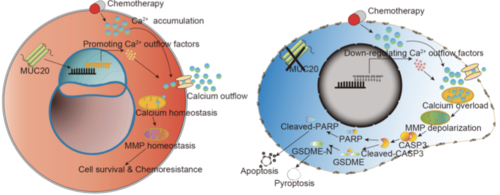
- MUC20v2 enhanced cell survival ability and chemoresistance by maintaining mitochondrial calcium levels and mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP).
- MUC20v2 protected SRCC cells from apoptosis and pyroptosis, not ferroptosis.
Abstract
Signet ring cell carcinoma (SRCC) is a specific histologic variant in gastric cancer (GC). We analyzed a comprehensive GC cell line database to identify the specifically expressed genes in SRCC. Among the 16 genes highly expressed in SRCC based on the analysis, we investigated the role of MUC20 in SRCC progression. First, cohort analysis revealed that GC patients with high-MUC20 expression exhibited a poor prognosis and that MUC20 expression was significantly correlated with SRCC histological type. Moreover, we found that SRCC cells specifically expressed MUC20 variant 2 (MUC20v2), which was dominantly expressed in the cytoplasm. Silencing MUC20v2 caused cell death with characteristic morphological changes in SRCC cells. To further determine the types of cell death, we assessed apoptosis, pyroptosis and ferroptosis by detecting cleaved PARP, gasdermin E-N-terminal, and lipid reactive oxygen species levels, respectively. We found that apoptosis and pyroptosis occurred in MUC20-silenced SRCC cells. However, MUC20v2-overexpressing GC cells exhibited chemoresistance to cisplatin and paclitaxel. In addition, RNA sequencing revealed that pathways involved in intracellular calcium regulation were significantly upregulated in MUC20v2-overexpressing GC cells. Notably, forced expression of MUC20v2 led to the maintenance of mitochondrial calcium homeostasis and mitochondrial membrane potential, which resulted in cell survival and chemoresistance by suppressing apoptosis and pyroptosis. Finally, we investigated the significance of MUC20v2 in a xenograft model treated with cisplatin and showed that MUC20v2 overexpression caused chemoresistance by inhibiting cell death. These findings highlight the novel potential functions of MUC20v2 in conferring cell survival and drug resistance in GC cells.
Representative Figure