- HOME
- News & Events
- Publications
- 【Publications】Rapid point-of-care test for hepatitis B core-related antigen to diagnose high viral l...
Publications
【Publications】Rapid point-of-care test for hepatitis B core-related antigen to diagnose high viral load in resource-limited settings
June 14 2022
Yusuke Shimakawa
Paper information
Title:
Rapid point-of-care test for hepatitis B core-related antigen to diagnose high viral load in resource-limited settings
Yusuke Shimakawa,1,2 Gibril Ndow,3,4 Atsushi Kaneko,5 Katsumi Aoyagi,5 Maud Lemoine,4 Yasuhito Tanaka,6 and PROLIFICA/HBcrAg-RDT Study Group
* PROLIFICA/HBcrAg-RDT Study Group: Théo Cerceau,1 Amie Ceesay,3 Akira Hasegawa,5 Naoki Yamamoto,5 Jeanne Perpétue Vincent,1 Takehisa Watanabe,6 Masaya Baba,2 Bakary Sanneh,7 Ignatius Baldeh,7 Ramou Njie,8,9 Umberto D'Alessandro,3 Maimuna Mendy,10 Isabelle Chemin,11 and Mark R. Thursz4
1 Unité d'Épidémiologie des Maladies Émergentes, Institut Pasteur, Paris, France
2 International Research Center for Medical Sciences (IRCMS), Kumamoto University, Kumamoto, Japan
3 Medical Research Council (MRC) Unit The Gambia at the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, Fajara, The Gambia
4 Department of Metabolism, Digestion & Reproduction, Imperial College London, UK
5 Research and Development Division, Fujirebio Inc., Tokyo, Japan
6 Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Faculty of Life Sciences, Kumamoto University, Kumamoto, Japan
7 National Public Health Laboratories, Ministry of Health, The Gambia
8 Edward Francis Small Teaching Hospital, Banjul, The Gambia
9 School of Medicine & Allied Health Sciences, University of The Gambia
10 International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), Lyon, France
11 INSERM U1052, CNRS UMR5286, Centre de Recherche en Cancérologie, Université Claude Bernard, Lyon, France
Clinical Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2022 June 10.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2022.05.026
Highlights
- To globally eliminate hepatitis B, it is crucial to scale up testing and treatment services in resource-limited countries with high HBV prevalence.
- However, access to nucleic acid testing (NAT) to quantify HBV DNA levels, an essential test to assess treatment eligibility, is hardly available and affordable in these countries.
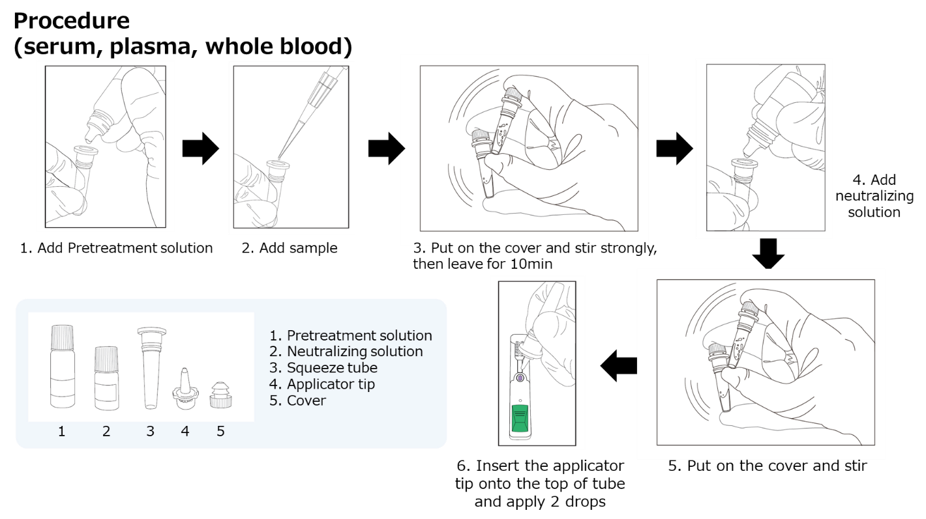
- We developed a simple, low-cost, equipment-free, lateral flow rapid diagnostic test (RDT) to detect HBcrAg (HBcrAg-RDT) using serum, plasma, or whole blood.
- In 284 treatment-naïve patients with chronic HBV infection in West Africa, HBcrAg-RDT had a sensitivity and specificity of 72.7% and 91.7% to diagnose HBV DNA levels of ≥2,000 IU/ml, 86.7% and 88.7% for ≥20,000 IU/ml, and 91.4% and 86.3% for ≥200,000 IU/ml, respectively.
- A simplified HBV DNA-free treatment algorithm using HBcrAg-RDT had a sensitivity of 93.2% and specificity of 86.7% to identify HBV-infected patients eligible for antiviral therapy by the AASLD criteria.
- HBcrAg-RDT is an accurate, rapid (45 minutes) and inexpensive (<5 USD) tool to easily distinguish patients with high HBV DNA levels from those with low viral loads.