- HOME
- News & Events
- Publications
- 【Publications】Targeting chemoresistance in Xp11.2 translocation renal cell carcinoma using a novel p...
Publications
【Publications】Targeting chemoresistance in Xp11.2 translocation renal cell carcinoma using a novel polyamide-chlorambucil conjugate
April 20 2022
Masaya Baba
Paper information
Title:
Targeting chemoresistance in Xp11.2 translocation renal cell carcinoma using a novel polyamide-chlorambucil conjugate
Shintaro Funasaki, Sally Mehanna, Wenjuan Ma, Hidekazu Nishizawa, Yasuhiko Kamikubo, Hiroshi Sugiyama, Shuji Ikeda, Takanobu Motoshima, Hisashi Hasumi, W. Marston Linehan, Laura S Schmidt, Chris Ricketts, Toshio Suda, Yuichi Oike, Tomomi Kamba, Masaya Baba
Cancer Science 2022 Apr 9.
doi: 10.1111/cas.15364. Online ahead of print URL: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/cas.15364
Highlights
- Renal cell carcinoma with Xp11.2 translocation involving TFE3 gene (TFE3-RCC) is a recently identified subset of RCC, in which the chimeric TFE3 transcriptionally activates its downstream target genes.
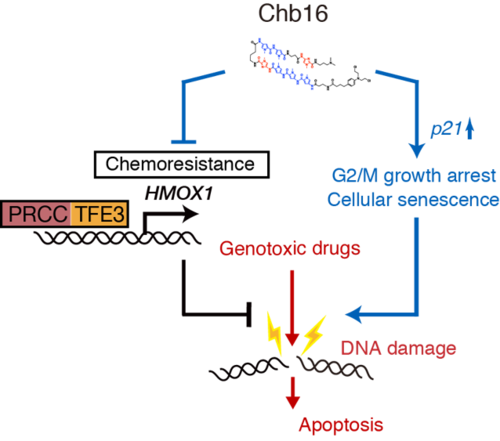
- We show that PRCC-TFE3, a chimeric TFE3, confers chemo resistance by regulating heme oxygenase 1 (HMOX1) expression in TFE3-RCC.
- We generated, Chb16, a novel chlorambucil-polyamide conjugate (Chb) to target PRCC-TFE3 dependent transcription and identified Chb16 as a PRCC-TFE3-dependent transcriptional inhibitor of HMOX1 expression.
- Treatment of patient-derived TFE3-RCC cells with Chb16 resulted in senescence and growth arrest and increased sensitivity to the genotoxic reagent etoposide.
- TFE3-RCC cells acquired chemoresistance through HMOX1 expression and inhibition of HMOX1 by Chb16 may be an effective therapeutic strategy against TFE3-RCC.
Abstract
Renal cell carcinoma with Xp11.2 translocation involving TFE3 gene (TFE3-RCC) is a recently identified subset of RCC with unique morphology and clinical presentation. The chimeric PRCC-TFE3 protein produced by Xp11.2 translocation has been shown to transcriptionally activate its downstream target genes that play important roles in carcinogenesis and tumor development of TFE3-RCC. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms remain poorly understood. Here we show that in TFE3-RCC cells, PRCC-TFE3 controls heme oxygenase 1 (HMOX1) expression to confer chemoresistance. Inhibition of HMOX1 sensitized the PRCC-TFE3 expressing cells to genotoxic reagents. We screened for a novel chlorambucil-polyamide conjugate (Chb) to target PRCC-TFE3 dependent transcription, and identified Chb16 as a PRCC-TFE3-dependent transcriptional inhibitor of HMOX1 expression. Treatment of the patient derived cancer cells with Chb16 exhibited senescence and growth arrest, and increased sensitivity of the TFE3-RCC cells to the genotoxic reagent etoposide. Thus, our data showed that the TFE3-RCC cells acquired chemoresistance through HMOX1 expression and that inhibition of HMOX1 by Chb16 may be an effective therapeutic strategy for TFE3-RCC.
Implications
The identification of novel inhibitors based on PIP-Chb is expected to provide the basis for effective therapies for advanced TFE3 fusion RCC and other types of translocation RCC tumors through targeting chemotherapy resistance.
The proposed mechanism by which PRCC-TFE3 RCC cells acquire chemoresistance and the effect of Chb16.
Briefly, PRCC-TFE3 confers chemoresistance through expression of downstream genes including HMOX1. Chb16 inhibits its transcription to reduce chemoresistance from genotoxic agents such as etoposide. Chb16 also exhibits DNA stress to enhance the cytotoxicity of a cancer drug such as etoposide.