- HOME
- News & Events
- Publications
- 【Publications】Blood and lymphatic systems are segregated by the FLCN tumor suppressor
Publications
【Publications】Blood and lymphatic systems are segregated by the FLCN tumor suppressor
December 11 2020
Masaya Baba
Paper information
Ikue Tai-Nagara, Yukiko Hasumi, Dai Kusumoto, Hisashi Hasumi, Keisuke Okabe, Tomofumi Ando, Fumio Matsuzaki, Fumiko Itoh, Hideyuki Saya, Chang Liu, Wenling Li, Yoh-suke Mukouyama, W. Marston Linehan, Xinyi Liu, Masanori Hirashima, Yutaka Suzuki, Shintaro Funasaki, Yorifumi Satou, Mitsuko Furuya, Masaya Baba*, Yoshiaki Kubota* (* corresponding authors)
Blood and lymphatic systems are segregated by the FLCN tumor suppressor
Nature Communications. 2020 December 9. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20156-6 . URL: https://rdcu.be/cbUbc
Highlights
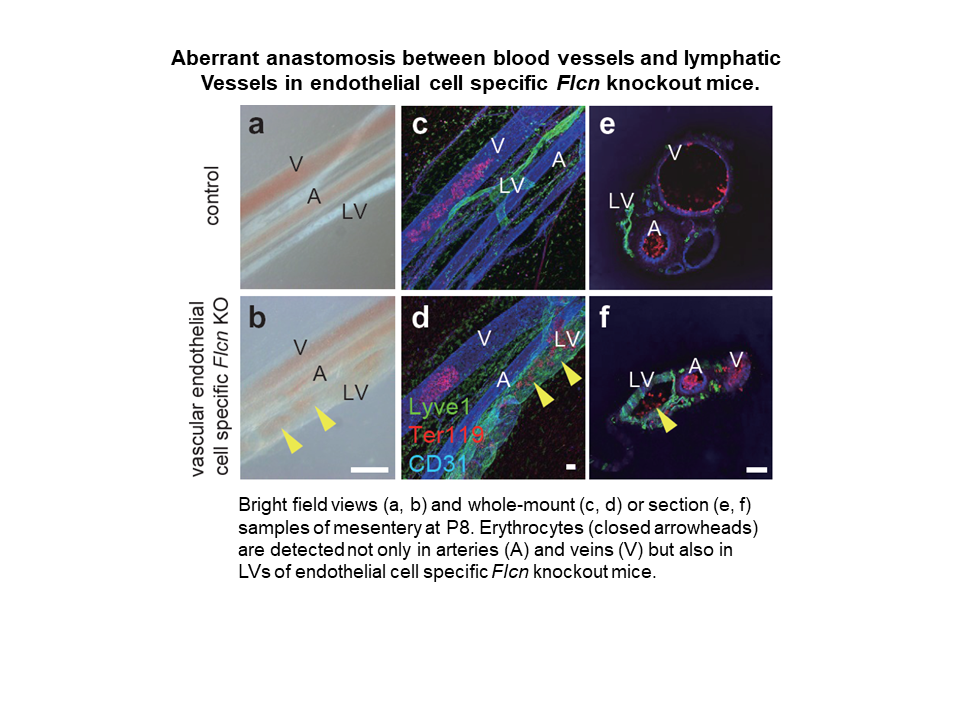
- Blood vessel (BV) and lymphatic vessel (LV) are discretely distributed throughout the body without sharing the same lumen. The molecular mechanisms that ultimately maintain separation of these two circulatory systems have not been fully identified.
- We show that genetic deficiency of Folliculin (FLCN) , a tumor suppressor, leads to misconnection of blood and lymphatic vessels in mice and humans.
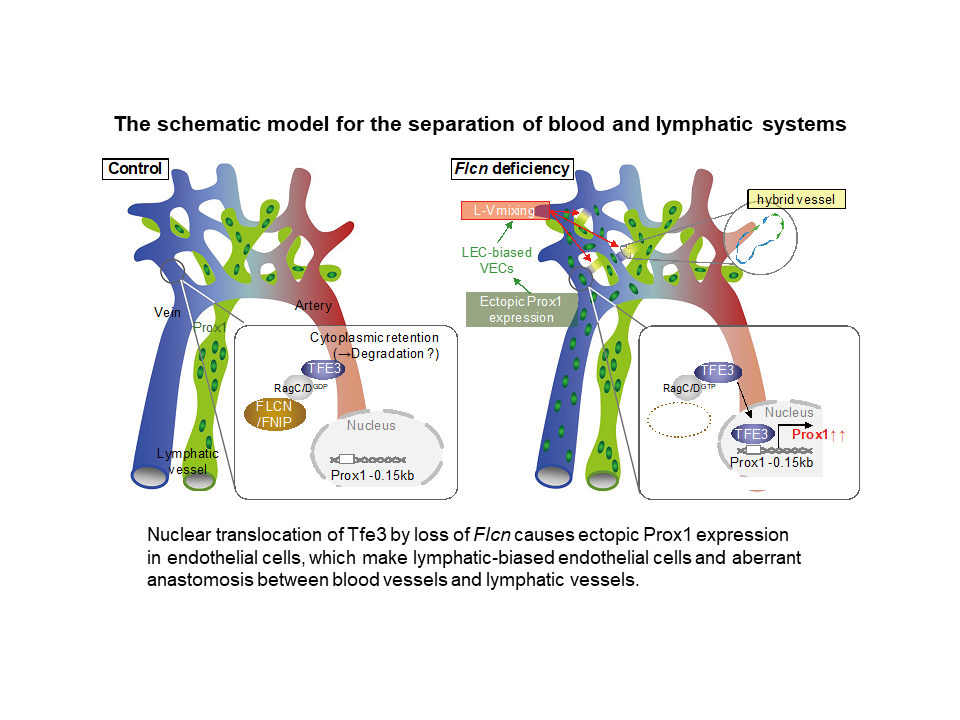
- Loss of Flcn in endothelial cells caused ectopic expression of Prox1 which was mediated by aberrant Tfe3 activation and resulted in the appearance of lymphatic-biased venous endothelial cells.
- Folliculin acts as a gatekeeper that maintains separation of blood and lymphatic vessels by limiting the plasticity of committed endothelial cells.
Abstract
Blood and lymphatic vessels structurally bear a strong resemblance but never share a lumen, thus maintaining their distinct functions. Although lymphatic vessels initially arise from embryonic veins, the molecular mechanism that maintains separation of these two systems has not been elucidated. Here, we show that genetic deficiency of Folliculin, a tumor suppressor, leads to misconnection of blood and lymphatic vessels in mice and humans. Absence of Folliculin results in the appearance of lymphatic-biased venous endothelial cells caused by ectopic expression of Prox1, a master transcription factor for lymphatic specification. Mechanistically, this phenotype is ascribed to nuclear translocation of the basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor Transcription Factor E3 (TFE3), binding to a regulatory element of Prox1, thereby enhancing its venous expression. Overall, these data demonstrate that Folliculin acts as a gatekeeper that maintains separation of blood and lymphatic vessels by limiting the plasticity of committed endothelial cells.
Implications
These findings may provide the foundation for the development of novel therapeutic approaches for human lymphatic disorders as well as to prevent cancer metastasis.