- HOME
- News & Events
- Publications
- 【Publications】Loss of Folliculin Disrupts Hematopoietic Stem Cell Quiescence and Homeostasis Resulti...
Publications
【Publications】Loss of Folliculin Disrupts Hematopoietic Stem Cell Quiescence and Homeostasis Resulting in Bone Marrow Failure
June 29 2016
Masaya Baba
Paper information
Masaya Baba, Hirofumi Toyama, Lei Sun, Keiyo Takubo, Hyung-Chan Suh, Hisashi Hasumi, Ayako Nakamura-Ishizu, Yukiko Hasumi, Kimberly D. Klarmann, Naomi Nakagata, Laura S. Schmidt, W. Marston Linehan, Toshio Suda, and Jonathan R. Keller
Loss of Folliculin Disrupts Hematopoietic Stem Cell Quiescence and Homeostasis Resulting in Bone Marrow Failure.
Stem Cells. 34(4):1068-82, 2016
Highlights
*Folliculin (FLCN) is a tumor suppressor gene which encodes an essential multifunctional protein FLCN.
*Flcn is required for the development of myeloid, erythroid and lymphoid lineages.
*Loss of Flcn causes proliferative exhaustion of hematopoietic stem cells resulting in bone marrow failure.
*mTORC1 and Tfe3 activation contribute to the phenotype of Flcn knockout in bone marrow.
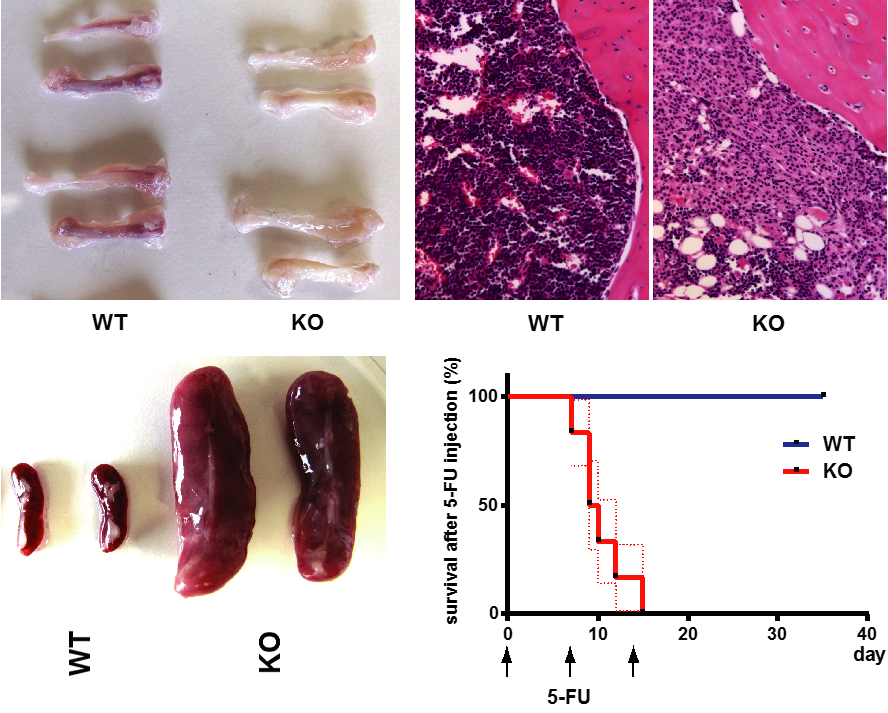
Abstract
Folliculin (FLCN) is an autosomal dominant tumor suppressor gene that modulates diverse signaling pathways required for growth, proliferation, metabolism, survival, motility, and adhesion. FLCN is an essential protein required for murine embryonic development, embryonic stem cell (ESC) commitment, and Drosophila germline stem cell maintenance, suggesting that Flcn may be required for adult stem cell homeostasis. Conditional inactivation of Flcn in adult hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (HSPCs) drives hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) into proliferative exhaustion resulting in the rapid depletion of HSPC, loss of all hematopoietic cell lineages, acute bone marrow (BM) failure, and mortality after 40 days. HSC that lack Flcn fail to reconstitute the hematopoietic compartment in recipient mice, demonstrating a cell-autonomous requirement for Flcn in HSC maintenance. BM cells showed increased phosphorylation of Akt and mTorc1, and extramedullary hematopoiesis was significantly reduced by treating mice with rapamycin in vivo, suggesting that the mTorc1 pathway was activated by loss of Flcn expression in hematopoietic cells in vivo. Tfe3 was activated and preferentially localized to the nucleus of Flcn knockout (KO) HSPCs. Tfe3 overexpression in HSPCs impaired long-term hematopoietic reconstitution in vivo, recapitulating the Flcn KO phenotype, and supporting the notion that abnormal activation of Tfe3 contributes to the Flcn KO phenotype. FlcnKO mice develop an acute histiocytic hyperplasia in multiple organs, suggesting a novel function for Flcn in macrophage development. Thus, Flcn is intrinsically required to maintain adult HSC quiescence and homeostasis, and Flcn loss leads to BM failure and mortality in mice. Stem Cells 2016