- HOME
- News & Events
- Publications
- 【Publications】Relative resistance of HLA-B to down-regulation by naturally occurring HIV-1 Nef seque...
Publications
【Publications】Relative resistance of HLA-B to down-regulation by naturally occurring HIV-1 Nef sequences.
February 20 2016
Takamasa Ueno
Paper information
Mahiti M*, Toyoda M*, Jia X, Kuang X, Mwimanzi F, Mwimanzi F, Walker B, Xiong Y, Brumme ZL, Brockman M, Ueno T
*MM and TM contributed equally.
Relative resistance of HLA-B to down-regulation by naturally occurring HIV-1 Nef sequences. mBio 7(1):e01516-15. doi:10.1128/mBio.01516-15.
Highlights
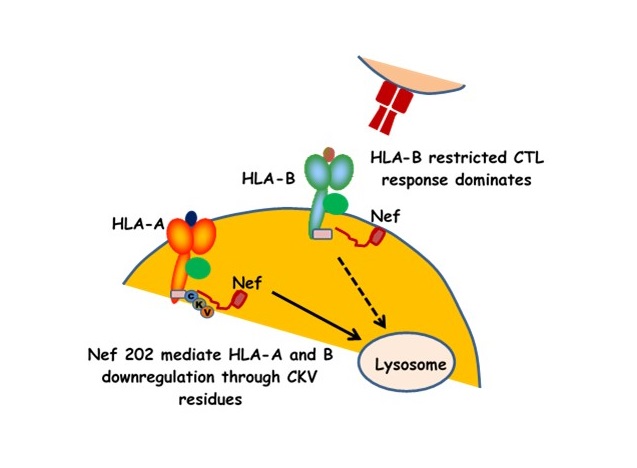
u Naturally isolated Nef clones differentially downregulate HLA-A and HLA-B.
u The amino acid residue at Nef-202 is responsible for differential sensitivity to HLA-A and HLA-B for downregulation.
u The C-terminal Cys-Lys-Val residues of HLA-A, which are absent in HLA-B are responsible for Nef's sensitivity to downregulation.
u The differential ability of Nef to downregulate HLA on HIV-infected cells modulates their subsequent recognition by HIV-specific T cells.
Abstract
HIV-1 Nef binds to the cytoplasmic region of HLA-A and HLA-B and down-regulates these molecules from the surface of virus-infected cells, thus evading immune detection by CD8+ T cells. Polymorphic residues within the HLA cytoplasmic region may affect Nef's down-regulation activity. However the impact of HLA polymorphisms on recognition by primary Nef isolates remains elusive, as do the specific Nef regions responsible for down-regulation of HLA-A versus HLA-B. Here, we examined 46 Nef clones isolated from chronically HIV-1 subtype B-infected subjects for their ability to down-regulate various HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-C molecules on the surface of virus-infected cells. Overall, HLA-B exhibited greater resistance to Nef-mediated down-regulation compared to HLA-A, regardless of cell type examined. As expected, no Nef clone down-regulated HLA-C. Importantly, the differential ability of patient-derived Nef clones to down-regulate HLA-A and HLA-B inversely correlated with the sensitivity of HIV-infected target cells to recognition by effector cells expressing an HIV-1 Gag-specific T cell receptor. Nef codon-function analysis implicated amino acid variation at position 202 (Nef-202) in differentially affecting HLA-A and HLA-B down-regulation ability, an observation that was subsequently confirmed by site-directed mutagenesis. In silico and mutagenesis analyses further suggested that Nef-202 may interact with the C-terminal Cys-Lys-Val residues of HLA-A, which are absent in HLA-B. Taken together, natural polymorphisms within Nef modulate its interaction with natural polymorphisms in the HLA cytoplasmic tails, thereby affecting the efficiency of HLA down-regulation and consequent recognition by HIV-specific T cells. Results thus extend our understanding of this complex pathway of retroviral immune evasion.