Shinya Suzu
Paper Information
Hashimoto M, Nasser H, Chihara T, Suzu S.
Macropinocytosis and TAK1 mediate anti-inflammatory to pro-inflammatory macrophage differentiation by HIV-1 Nef. Cell Death Dis. 2014 May 29;5:e1267.
http://www.nature.com/cddis/journal/v5/n5/full/cddis2014233a.html
Highlights
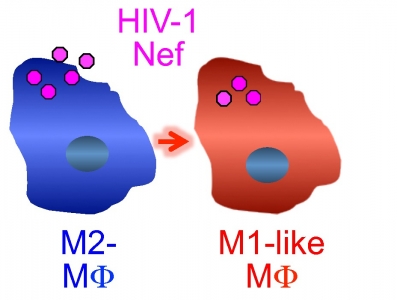
- HIV-1 pathogenetic protein Nef activates multiple signaling pathways preferentially in anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages.
- The signaling molecule TAK1 is required for this activity of Nef.
- Nef enters M2-macrophages by exploiting their higher macropinocytosis activity.
- Nef drives anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages towards pro-inflammatory M1-like macrophages.
Abstract
Macrophages (MΦ) are functionally classified into two types, anti-inflammatory M2 and pro-inflammatory M1. Importantly, we recently revealed that soluble HIV-1 proteins, particularly the pathogenetic protein Nef, preferentially activate M2-MΦ and drive them towards an M1-like MΦ, which might explain the sustained immune activation seen in HIV-1-infected patients. Here, we show that the preferential effect of Nef on M2-MΦ is mediated by TAK1 (TGF-β-activated kinase 1) and macropinocytosis. As with MAP kinases and NF-κB pathway, Nef markedly activated TAK1 in M-CSF-derived M2-MΦ but not in GM-CSF-derived M1-MΦ. Two Nef mutants, which were unable to activate MAP kinases and NF-κB pathway, failed to activate TAK1. Indeed, the TAK1 inhibitor 5Z-7-oxozeaenol as well as the ectopic expression of a dominant-negative mutant of TAK1 or TRAF2, an upstream molecule of TAK1, inhibited Nef-induced signaling activation and M1-like phenotypic differentiation of M2-MΦ. Meanwhile, the preferential effect of Nef on M2-MΦ correlated with the fact the Nef entered M2-MΦ more efficiently than M1-MΦ. Importantly, the macropinosome formation inhibitor EIPA completely blocked the internalization of Nef into M2-MΦ. Because the macropinocytosis activity of M2-MΦ was higher than that of M1-MΦ, our findings indicate that Nef enters M2-MΦ efficiently by exploiting their higher macropinocytosis activity and drives them towards M1-like MΦ by activating TAK1.