- HOME
- Education
- Student's Voice
- 【IRCMS Internship】Mr. Mohammad Nazmus Sakib (Jahangirnagar University)
Student's Voice

Name: Mohammad Nazmus Sakib
Jahangirnagar University
Visiting Period: February 26th (Mon) - March 18th (Mon), 2024
Country: Bangladesh
Lab: Laboratory of Chromatin Organization in Immune Cell Development
Objectives
The objective was to carry out different laboratory experiments that are part of current research projects. There were multiple experiments aiming to understand the immunological phenomena notably Irf8 expression in dendritic cells (Kurotaki et al., 2019) and delayed type dermatitis in mouse models.
Overview of experiences and skills developed at IRCMS
I performed and observed a series of experiments. Almost all experiments were done at IRCMS, although a little of them had to be conducted at IMEG (Institute of Molecular Embryology & Genetics). The experiments including the skills I have learned from doing internship at IRCMS so far are listed below:
- Fluorescence-activated Cell Sorting (FACS) analysis of dendritic cells of mouse spleen (SPL): I obtained hands-on training on how to collect SPL from mouse. Using different enzyme mixes such as DNase I and Liberase, I learned how to process the cells for FACS analysis. In the meantime, I also got to use both hemocytometer and automated cell counter to count the number of cells present in the sample. I also utilized the opportunity to use magnetic beads and utilized DynaMag for collecting the required fractions. Additionally, learned the principles of using markers such as CD19/CD3/Ly6G/NK1.1/CD115/B220 and perfectly demonstrating their usage in SORP Aria for sorting the cells. In this process, I got to see the usage of BD FACSAria Cell Sorter & BD FACSymphony Cell Analyzer. Finally, I had a brief introduction on how to perform compensation and gating as well as analyzing FACS-derived dataset. One of the goals of the experiment is to clarify which precursor differentiate into XCR1+ inflammatory DC and what functions they have (Anderson et al., 2021; Bosteels et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2023)
- Sorting different immune cells derived by cytokine injection: I had the opportunity to see the collection of lymph node from mice and preparing them for cell sorting.
- Hi-C method: I fixated the cells for Hi-C method using formaldehyde and other chemicals (Belton et al., 2012). After that, I learned to lyse the cells and used restriction enzymes (e.g. DpnII) for digestion. Got brief introduction to use ThermoMixer to gently prepare the samples for analysis. Next, filled in by Biotin and ligated the DNA by making use of different chemicals such as Klenow polymerase, Biotin-dATP, other dNTPs and proteinase K and quantitated the DNA by Qubit. I also have the process of using Bioanalyzer at IMEG to analyze the samples.
- Observing immune response in WT and dP2 mice:I have got brief introduction on the processing of mice with 1-Fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (DNFB) and measuring the thickness of ears of mice after anesthesia. I also learned the process of RNA extraction and purification from mouse ears and the measurement of concentration using Nanodrop. Therefore, I also got the opportunity to see the measurement of Irf8 expression in mouse ears after the stimulation and analysis of them by qPCR.
- RNA-seq analysis of PBS and IL-12 treated mice: I learned the preliminary usage of linux server and utilizing it for the analysis of RNA-seq data previously obtained. I learned to use fastqc, multiqc, salmon software and R packages for understanding the differentially expressed genes such as edgeR.
Results and achievements:
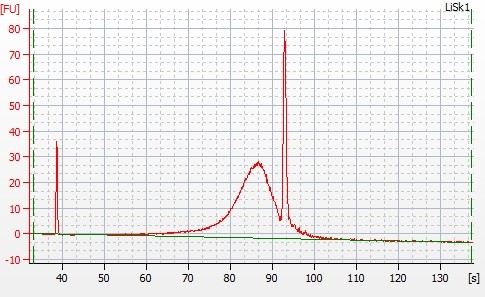
Figure 1: Bioanalyzer image about the ligation of DNA in day 4
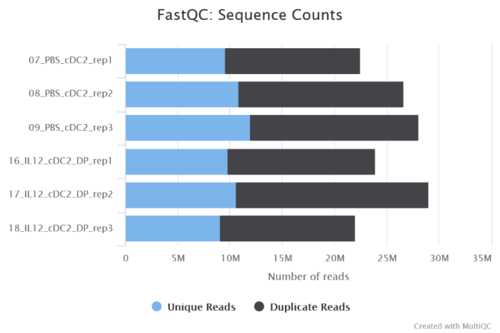
Figure 2: Reads including unique and duplicate ones are shown in MultiQC report
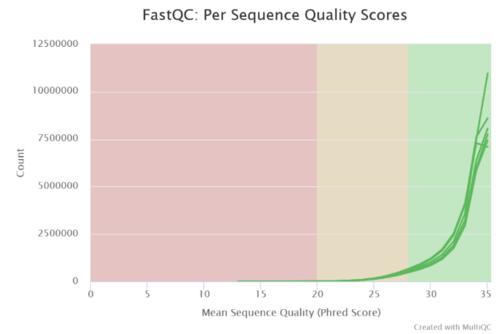
Figure 3: Phred score for sequence quality of six dataset are shown
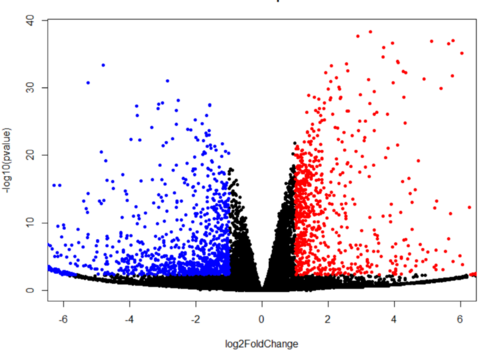
Figure 4: Generated volcano plot for visualization of upregulated and downregulated genes by R programming
Conclusion
Bioanalyzer image from day 4 depicted that ligation was done smoothly and can be utilized for further experiments. RNA-seq analysis showed the upregulated and downregulated genes. Further, these genes can be used for gene enrichment and clustering by metascape.
Acknowledgement
I express my heartfelt gratitude to Dr. Daisuke Kurotaki, Dr. Kenta Kikuchi and Ms. Anastasiia Shuliak for their invaluable guidance and support throughout my internship period. My sincere appreciation to the IRCMS for providing me with this incredible opportunity for understanding and learning something new in the field of my interest. I am also grateful to Mr. Samiul Alam Rajib who is a doctoral student at Joint Research Center for Human Retrovirus Infection, Kumamoto University for showing me around the city of Kumamoto.
References
Anderson, D. A., Dutertre, C. A., Ginhoux, F., & Murphy, K. M. (2021). Genetic models of human and mouse dendritic cell development and function. In Nature Reviews Immunology (Vol. 21, Issue 2). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41577-020-00413-x
Belton, J. M., McCord, R. P., Gibcus, J. H., Naumova, N., Zhan, Y., & Dekker, J. (2012). Hi-C: A comprehensive technique to capture the conformation of genomes. Methods, 58(3). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.05.001
Bosteels, C., Neyt, K., Vanheerswynghels, M., van Helden, M. J., Sichien, D., Debeuf, N., De Prijck, S., Bosteels, V., Vandamme, N., Martens, L., Saeys, Y., Louagie, E., Lesage, M., Williams, D. L., Tang, S. C., Mayer, J. U., Ronchese, F., Scott, C. L., Hammad, H., ... Lambrecht, B. N. (2020). Inflammatory Type 2 cDCs Acquire Features of cDC1s and Macrophages to Orchestrate Immunity to Respiratory Virus Infection. Immunity, 52(6). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2020.04.005
Kurotaki, D., Kawase, W., Sasaki, H., Nakabayashi, J., Nishiyama, A., Morse, H. C., Ozato, K., Suzuki, Y., & Tamura, T. (2019). Epigenetic control of early dendritic cell lineage specification by the transcription factor IRF8 in mice. Blood, 133(17). https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2018-06-857789
Liu, Z., Wang, H., Li, Z., Dress, R. J., Zhu, Y., Zhang, S., De Feo, D., Kong, W. T., Cai, P., Shin, A., Piot, C., Yu, J., Gu, Y., Zhang, M., Gao, C., Chen, L., Wang, H., Vétillard, M., Guermonprez, P., ... Ginhoux, F. (2023). Dendritic cell type 3 arises from Ly6C+ monocyte-dendritic cell progenitors. Immunity, 56(8). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2023.07.001